However, if we try to dissolve the non-polar vitamin D molecules in a polar solvent like water, the vitamin D will not dissolve.
Water molecules in the solvent are attracted to each other by the much stronger intermolecular forces known as hydrogen bonds.
So the water molecules are much more strongly attracted to each other than they are to the non-polar Vitamin D molecules.
As a result, non-polar vitamin D molecules are insoluble in water.
Exposure of our skin to sunlight (ultraviolet light) is necessary for the human body to produce the active form of vitamin D.
We only need to expose our skin to about 30 minutes of sunlight twice a week in order to produce adequate amounts of vitamin D.
We do not need daily exposure to sunlight because vitamin D, being a fat soluble vitamin, can be stored in fatty tissues of the liver in the human body.
1. Nutritionists also refer to "Minerals" which they define as essential nutrients that are NOT organic, that is, they are inorganic.
2. It is important to note that we are discussing human requirements because other animals are able to synthesise some vitamins.
3. Does it seem strange that the vitamins are named A, B, C, D, E .... and then ... K ?
This is because, over time, a molecule has ceased to be classified as a vitamin, or a molecule has been redesignated, for example, vitamin B7, or biotin, was previously designated as vitamin H.
Vitamin K1 was named the "coagulation vitamin" (koagulationsvitamin in German) when its role in preventing blood from coagulating was noted in 1929 by Danish scientist Henrik Dam.
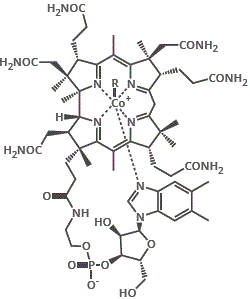
4. Nicotinic acid or nicotinamide (niacin or niacinamide) are the vitamins needed for cofactor NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), a biological oxidising agent.
5. Pantothenic acid is the vitamin required for cofactor coenzyme A (acetyl CoA), involved in carbohydrate metabolism.
6. Pyridoxine is the vitamin needed for cofactor pyridoxyl phosphate
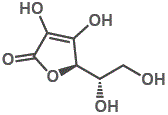
7. "Vitamin C" refers to the ascorbic acid molecule as well as to the ascorbate salts, and even to some oxidised forms of the molecule such as dehydroascorbic acid.
In each case, "Vitamin C" refers to the L-enantiomer. The D-enantiomer is not found in nature.
8. It is estimated that scurvy killed at least 2 million sailors between 1500 and 1800. Lind, a Scottish surgeon who sailed with the Royal Navy became the first to show the efficacy of citrus juice in combatting the disease in 1747, but it took another 50 years before his findings were generally accepted.
Because British sailors from the mid-nineteenth century were given a daily dose of lime juice to guard against scurvy, they came to be known as "limeys".
9. Other organic compounds included in the vitamin A group are retinal, retinoic acid, and carotenoids like beta-carotene.
10. Other D-group vitamins include vitamin D4 (2,2-dihydroergocalciferol) and vitamin D5 (sitocalciferol).
The major forms of vitamin D are vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol), and together they are referred to as vitamin D or calciferol.
11. electronegativity by Pauling's method


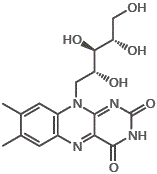
 nicotinic acid
nicotinic acid nicotineamide
nicotineamide