| Type: Flame Tests | |
| Features |
Uses |
- inexpensive
- fast, but some colours may be masked by others making it unreliable
- qualitative technique
- limited application as many common metals (e.g., Al & Mg) do not colour a flame
- a type of emission spectroscopy which can be observed by the naked eye or by using a spectroscope to see a series of bright lines
|
Identification of metals in some salts
- Li+ crimson
- Na+ yellow
- K+ lilac
- Ca2+ brick red
- Sr2+ scarlet
- Ba2+ green
- Cu2+ green-blue
|
|
| Type: Colorimetry | |
| Features |
Uses |
- relatively inexpensive
- fast, requiring a set of standard solutions
- qualitative & quantitative
- a type of absorption spectroscopy limited to coloured solutions or compounds
|
- copper(II) sulfate in garden sprays
- iron(III) concentration using KSCN to form the coloured Fe(CNS)2+ complex
- coloured solutions such as food colourings
|
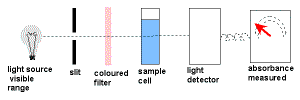 wavelength of light is selected for maximum absorbance & a calibration curve is constructed of absorbance versus concentration wavelength of light is selected for maximum absorbance & a calibration curve is constructed of absorbance versus concentration |
|
| Type: Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) | |
| Features |
Uses |
- expensive
- fast, requiring a set of standard solutions
- quantitative
- a type of absorption spectroscopy that can be used for all metals and metalloids (semi-metals)
|
- mercury in shellfish
- lead in soil samples
- trace metals in mineral waters
|
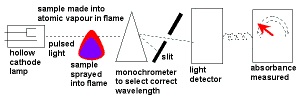 correct hollow cathode tube selected & a calibration curve constructed of absorbance versus concentration. (solutions may have to be diluted) correct hollow cathode tube selected & a calibration curve constructed of absorbance versus concentration. (solutions may have to be diluted) |
|
| Type: UV-Visible Spectroscopy | |
| Features |
Uses |
- expensive
- fast, requiring a set of standard solutions
- qualitative & quantitative
- a type of absorption spectroscopy limited to coloured solutions or compounds
|
- concentration of some coloured pharmaceuticals in blood serum
- concentration of metal ions using coloured complexes
- concentration of food colourings
|
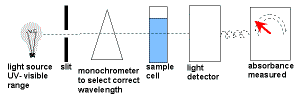 wavelength of light selected for maximum absorbance and a calibration curve constructed of absorbance versus concentration wavelength of light selected for maximum absorbance and a calibration curve constructed of absorbance versus concentration |

 wavelength of light is selected for maximum absorbance & a calibration curve is constructed of absorbance versus concentration
wavelength of light is selected for maximum absorbance & a calibration curve is constructed of absorbance versus concentration correct hollow cathode tube selected & a calibration curve constructed of absorbance versus concentration. (solutions may have to be diluted)
correct hollow cathode tube selected & a calibration curve constructed of absorbance versus concentration. (solutions may have to be diluted) wavelength of light selected for maximum absorbance and a calibration curve constructed of absorbance versus concentration
wavelength of light selected for maximum absorbance and a calibration curve constructed of absorbance versus concentration