Please do not block ads on this website.
No ads = no money for us = no free stuff for you!
Saponification
Example
glyceryl tristearate
(ester) |
+ |
NaOH
(base) |
→ |
glycerol
(alkanol) |
+ |
sodium stearate
(salt, soap) |
| |
H
| |
|
O
|| |
|
| H- |
C |
- O- |
C |
-(CH2)16-CH3 |
| |
| |
|
O
|| |
|
| H- |
C |
- O- |
C |
-(CH2)16-CH3 |
| |
| |
|
O
|| |
|
| H- |
C |
- O- |
C |
-(CH2)16-CH3 |
| |
|
H |
|
|
|
|
+ |
3NaOH |
→ |
| |
H
| |
|
| H- |
C |
-OH |
| |
| |
|
| H- |
C |
-OH |
| |
| |
|
| H- |
C |
-OH |
| |
|
H |
|
|
+ |
3CH3(CH2)16COO-Na+ |
Most soaps are made from vegetable oils such as olive oil, palm oil and coconut oil.
Some soaps are made from animal fats (tallows).
Potassium soaps tend to be softer and more water-soluble than the corresponding sodium soap.
Soaps from unsaturated fatty acids are softer than those from saturated fatty acids.
Cleaning Action of Soaps
When a soap such as sodium stearate dissolves in water, carboxylate anions and metal cations are produced:
| CH3(CH2)16COO-Na+ | water
→ | CH3(CH2)16COO-(aq) + Na+(aq) |
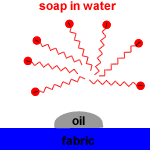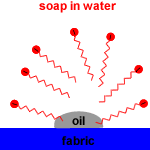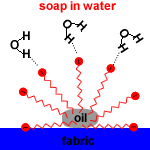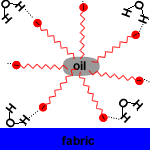
The non-polar, hydrophobic, long hydrocarbon chain end of the carboxylate ion attaches to non-polar dirt, grease and oil.
The hydrophilic, carboxylate anion end is attracted to polar water molecules by ion-dipole interactions.
Soap micelles, clusters of soap molecules in which the hydrocarbon chains are attracted to each other by Van der Waals forces (dispersion forces, London forces, weak intermolecular forces), surround the non-polar dirt particle, with the anion heads attracted to the surrounding water.
When agitated, the soil particle surrounded by soap micelles breaks free and remains dispersed in the washing water because the carboxylate anions repel each other.
The soil particle surrounded by soap micelles forms an emulsion in the washing water. An emulsion is a suspension of one liquid in another liquid. Soap is an emulsifying agent because it allows oil to be suspended in water.
As a cleaning agent, soap suffers from two main drawbacks:
- it does not function well in acidic solutions because of the formation of insoluble fatty acid
eg, CH3(CH2)16COO-Na+(aq) + HCl(aq) → CH3(CH2)16COOH(s) + Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
- it forms insoluble precipitates with Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions present in hard water, forming a scum
eg, 2CH3(CH2)16COO-Na+(aq) + Ca2+(aq) → [CH3(CH2)16COO-]2Ca2+(s) + 2Na+(aq)
Additives such as sodium carbonate and phosphates can help offset these effects.
Synthetic detergents are increasingly being used instead of soaps because they do not suffer from these disadvantages to the same extent.

