Structure and Formula of Silicates Chemistry Tutorial
Key Concepts
- The basic building block, the structural unit, of silicate minerals is the SiO44- tetrahedron.
- In the SiO44- tetrahedron each Si atom is covalently bonded to 4 oxygen atoms.
- In the tetrahedron Si has an oxidation state of +4 and O has an oxidation state of -2.
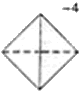
Overall charge on the tetrahedron = +4 + (4 × -2) = -4
- The SiO44- tetrahedron can be represented in different ways.
Some examples of different representations of the same SiO44- tetrahedron are shown below: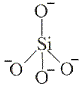
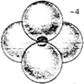
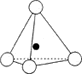
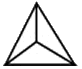
- The tetrahedra can link together by sharing corners resulting in Si-O-Si covalent bonds.
A number of different structures are therefore possible.
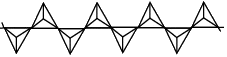
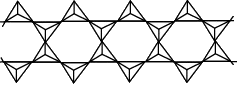
The table below shows how the tetrahedra join to form rings, chains, bands and sheets:discrete "molecules" 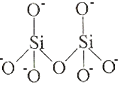

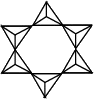
discrete rings 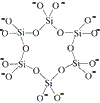
infinite single chains 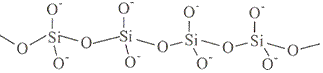
infinite double chains (bands) 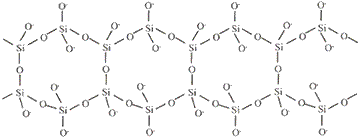
infinite sheets 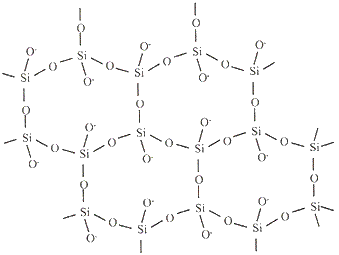
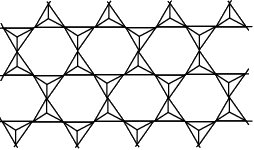
infinite three dimensional frameworks (or networks) - The formula of a silicate anion in a discrete "molecule" is given by the number of silicon atoms and the number of oxygen atoms in the structure:
structure structural formula molecular formula single tetrahedron 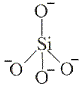
SiO44-
charge= +4 + (4×-2)
charge = 4-2 tetrahedra sharing a corner 
Si2O76-
charge = (2 × +4) + (7 × -2)
charge = 6-3 tetrahedra in a ring 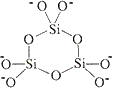
Si3O96-
charge = (3 × +4) + (9 × -2)
charge = 6-6 tetrahedra in a ring 
Si6O1812-
charge = (6 × +4) + (18 × -2)
charge = 12- - The formula of a silicate anion in an infinite array can be derived from the repeating unit within the structure:
structure repeating unit shown in red box formula infinite single chain 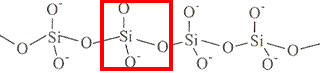
SiO32-
charge = +4 + (3 × -2)
charge = -2infinite double chain
(band)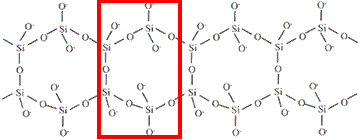
Si4O116-
charge = (4 × +4) + (11 × -2)
charge = -6infinite sheet 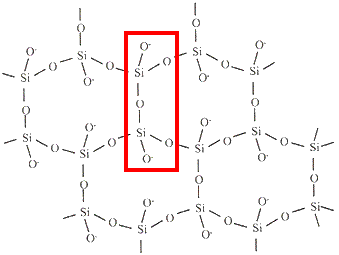
Si2O52-
charge = (2 × +4) + (5 × -2)
charge = -2infinite three dimensional framework (network) SiO2
charge = +4 + (2 × -2)
charge =0 - Cations are required to balance the charge on the silicate tetrahedra (compensating cations).
Some typical compensating cations are: sodium ions Na+ potassium ions K+ magnesium ions Mg2+ calcium ions Ca2+ aluminium ions Al3+

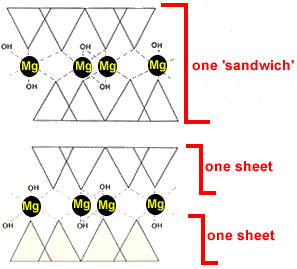 The mineral talc is made up of a 'sandwich'of two sheets of tetrahedra with the bases forming the outside of the sandwich as shown in the diagram on the right.
The mineral talc is made up of a 'sandwich'of two sheets of tetrahedra with the bases forming the outside of the sandwich as shown in the diagram on the right.