Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure of Gases Chemistry Tutorial
Key Concepts
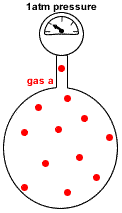
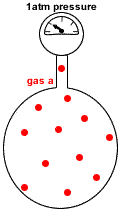
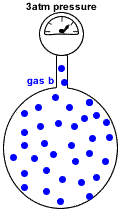
- Partial pressure of a gas in a mixture of gases is the pressure which that gas would exert if it were the only gas present in the container.
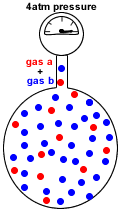
- Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures states that the total pressure in a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas:
P(total) = P(gas a) + P(gas b) + P(gas c) + etc
where:
P(total) = the total pressure exerted by the mixture of gases
P(gas a) = pressure exerted just by gas a
P(gas b) = pressure exerted just by gas b
P(gas c) = pressure exerted just by gas c
- Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures assumes each gas in the mixture is behaving like an ideal gas.