Acid Dissociation Constants (Ka) Chemistry Tutorial
Key Concepts
- Ka, the acid dissociation constant or acid ionisation constant, is an equilibrium constant that refers to the dissociation, or ionisation, of an acid.
- For the reaction in which the acid HA dissociates to form the ions H+ and A-:
HA
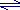 H+ + A-
H+ + A-
Ka = [H+][A-]
[HA] - Ka provides a measure of the equilibrium position
(i) if Ka is large, the products of the dissociation reaction are favoured
(ii) if Ka is small, undissociated acid is favoured.
- Ka provides a measure of the strength of an acid
(i) if Ka is large, the acid is largely dissociated so the acid is strong
(ii) if Ka is small, very little of the acid is dissociated so the acid is weak.
- The degree to which an acid dissociates, or ionizes, can be represented as a percentage:
% dissociation (ionization) = [H+ at equilibrium]
[acid initial]× 100 (i) If %dissociation ≈ 100%, the acid is a strong acid
(ii) If %dissociation is small, the acid is a weak acid
