Hall-Heroult Cell for the Production of Aluminium Chemistry Tutorial
Key Concepts
- Pure alumina, Al2O3, is extracted from the mineral bauxite using hot concentrated sodium hydroxide solution in the Bayer Process.
Amphoteric alumina dissolves in the sodium hydroxide while other substances present such as iron oxides and silicates do not dissolve.
- Alumina has a very high melting point, 2045oC, so it is dissolved in cryolite, Na3AlF6, to lower the melting point to around 970oC.
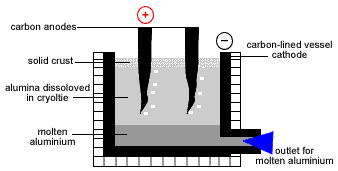
- Aluminium is produced by the electrolysis of molten alumina in a Hall-Heroult cell.
- A Hall-Heroult Cell is a carbon lined reaction vessel which acts as the cathode with carbon anodes dipped into the alumina-cryolite electrolyte.
- The amount of aluminium produced can be calculated using Faraday's Laws of Electrolysis.