The Greenhouse Gas Effect
Greenhouse gases in the earth's atmosphere absorb infrared radiation from the ground.
This radiation (heat) is re-emitted in all directions. Heat radiated back towards the earth's surface leads to the warming of the surface.
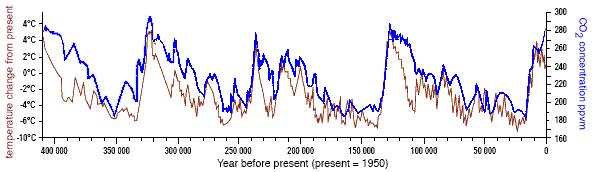
Using data from ice cores and other sources, scientists have been able to determine the temperature variation and carbon dioxide concentrations on earth over time:
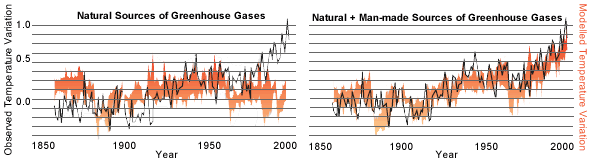
Since 1950, temperature variations have been observed that can not be explained solely on the basis of the presence of natural greenhouse gases.
Scientists have modeled this unusual temperature variation to take into account man-made sources of greenhouse gases and have found that this may explain the temperature variations being observed.
During the 21st century, the earth is likely to experience:
- higher maximum temperatures and more hot days
- higher minimum temperatures and fewer cold days
- more intense precipitation events like rain over many areas
- melting of polar ice caps resulting in rising sea levels
Suggestions for combatting global warming have been:
- reduction in combustion of fossil fuels and sourcing new fuel alternatives
- reducing deforestation and replanting forests
- reducing and/or eliminating the use of HCFs, HCFCs, perfluorocarbons and sulfur hexafluoride.
Finding alternatives to these greenhouse gases in chemical and industrial processes has led to the development of a new branch of chemistry called Green Chemistry.


