Conditions For Enzyme Function
Temperature
 Enzymes are highly sensitive to changes in temperature.
Enzymes are highly sensitive to changes in temperature.
In humans, most enzymes function best at body temperature (approximately 37oC).
In general, heating a reaction mixture speeds up the rate of reaction by increasing the number of successful collisions between reactant molecules. This is shown on the graph to the right before the optimum temperature for enzyme activity is reached.
If the temperature of the reaction is raised too high past the optimum temperature, the reaction rate decreases as the enzyme becomes denatured and loses its ability to function as a catalyst for the reaction.
pH
 Some enzymes can only act within a certain pH range.
Some enzymes can only act within a certain pH range.
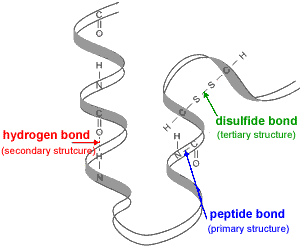
Outside this pH range the enzyme may become denatured, lose its tertiary structure, and therfore lose its ability to function as a catalyst for the reaction.

 Enzymes are highly sensitive to changes in temperature.
Enzymes are highly sensitive to changes in temperature.
 Some enzymes can only act within a certain pH range.
Some enzymes can only act within a certain pH range.