Structure of DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) Chemistry Tutorial
Key Concepts
- Nucleic acids are the carriers of genetic codes in living things.
- The two principal types of nucleic acids are deoxyribose nucleic acid (or deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA) and ribose nucleic acid (or ribonucleic acid, RNA).
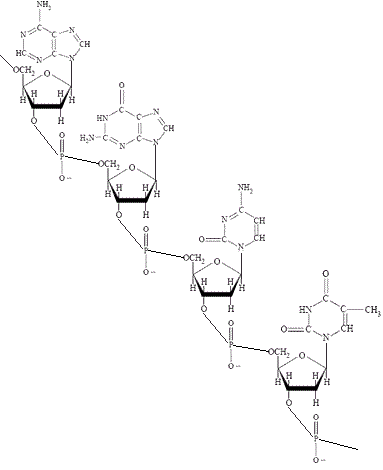
- DNA is a polymer.
- Individual monomer units are called nucleotides.
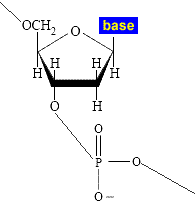
- The DNA polymer is composed of:
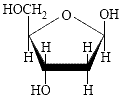
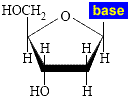
(i) a backbone of molecules of the sugar deoxyribose (a 5 carbon sugar)
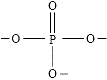
(ii) phosphate groups linking the deoxyribose sugar molecules together in a chain
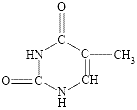
(iii) four principal bases (2 are pyrimidines and 2 are purines):
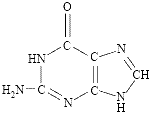
⚛ cytosine, a pyrimidine, abbreviated to C
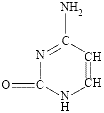
⚛ thymine, a pyrimidine, abbreviated to T
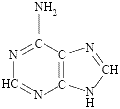
⚛ adenine, a purine, abbreviated to A
⚛ guanine, a purine, abbreviated to G
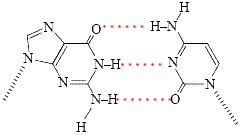
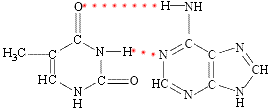
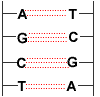
- The Watson-Crick model of DNA is that of a double helix of two long DNA molecules held together by hydrogen bonds.
- In this "double strand" of DNA, the principal bases occur in pairs with hydrogen bonding between them:
⚛ thymine-adenine pair formed by 2 hydrogen bonds
⚛ cytosine-guanine pair formed by 3 hydrogen bonds