Definitions of Acids and Bases Tutorial
Key Concepts
- Many substances can be classified as either acids or bases based on their properties.
- The definition of what an acid or a base is, is dependent on the chemical system being studied.
For aqueous solutions, acids are often defined by their ability to produce hydrogen ions (H+, also known as protons or hydrons)1.
- The definition that is most useful for students of Chemistry working with aqueous solutions2 is the definition proposed by Brønsted and Lowry independently in 1923 (also known as the Brønsted-Lowry definition, or Brønsted-Lowry theory, or the Lowry-Brønsted definition, or Lowry-Brønsted theory):
An acid is a substance that can donate a hydrogen ion,
that is, an acid is a proton donor.A base is a substance that can accept a hydrogen ion, that is,
a base is a proton acceptor. - When a Brønsted-Lowry acid donates (loses) a proton it produces a hydrogen ion (proton) and a conjugate base:
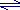
acid → proton + conjugate base HB → H+ + B- - When a Brønsted-Lowry base accepts (gains) a proton it produces a conjugate acid:
base + proton → conjugate acid B- + H+ → HB - A monoprotic acid is a Brønsted-Lowry acid that can only donate 1 proton :
HA → H+ + A-
A diprotic acid is a Brønsted-Lowry acid that can donate 2 protons :H2A → 2H+ + A-
A triprotic acid is a Brønsted-Lowry acid that can donate 3 protons :H3A → 3H+ + A-
The term polyprotic is used to describe any Brønsted-Lowry acid that is capable of donating more than 1 proton. - An amphiprotic substance is one that can either donate or accept a proton.
The definition of an amphiprotic substance is based on the Brønsted-Lowry definition of acids and bases.
HB- donating a proton
Brønsted-Lowry AcidHB- accepting a proton
Brønsted-Lowry Baseacid → proton + conjugate base base + proton → conjugate acid HB- → H+ + B2- HB- + H+ → H2B HB- is amphiprotic, it can either accept a proton to form H2B, or, it can donate a proton to form B2- - The term "amphoteric substance" is derived from an earlier definition of acids and bases proposed by Arrhenius:
An amphoteric substance is one that can act as either an Arrhenius acid, or, as an Arrhenius base:Arrhenius acids produce protons in aqueous solution :
HA → H+(aq) + A-(aq)Arrhenius bases produce hydroxide ions in aqueous solution:
BOH → OH-(aq) + B+(aq)An Arrhenius acid reacts with an Arrhenius base (OH-(aq)) to produce a salt.
An Arrhenius base reacts with an Arrhenius acid (H+(aq)) to produce a salt.An amphoteric substance can therefore react with either an Arrhenius acid (H+(aq)), or, with an Arrhenius base (OH-(aq)) to produce a salt.
- Unless otherwise stated, or implied, the terms acid and base as used in High School Chemistry will refer to Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases.
For example, if the definition being used in a particular example is that of Arrhenius, the acid will be stated to be an Arrhenius acid.
If a question refers to an amphoteric substance, the implication is that the Arrhenius definition of acids and bases is being used.

 H+ + B-
H+ + B-