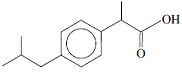
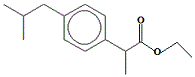
| Preparing the alcohol solvent by neutralising any acid that may be present:3
Step 1: Fill a burette with 0.10 mol L-1 NaOH(aq).
Step 2: Add 50 mL of glycerol (1,2,3-propanetriol) and 50 mL of hot water to a conical flask and heat the mixture to about 60oC.
Step 3: Add a couple of drops of phenolphthalein indicator to the warm solution in the conical flask.
Step 4: Add the NaOH(aq) from the burette drop by drop to the flask, stirring vigorously, until a pink colour appears.
Performing the titration to determine the ibuprofen content of tablets
Step 1: Refill the burette with 0.10 mol L-1 NaOH(aq).
Step 2: Place a tablet in the flask containing the pink alcohol solution and crush the tablet with a glass stirring rod.
The solution in the flask should now be colourless.
Step 3: Add two drops of phenolphthalein indicator to the flask.
Step 4: Titrate the contents of the flask with the NaOH(aq) from the burette until a permanent pink colour appears. Record the titre.
Repeat the procedure above until concordant titres are recorded.
Calculate the average mass of ibuprofen in a tablet and compare this result with the manufacturer's claim as shown on the packet of tablets.
|
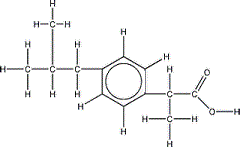

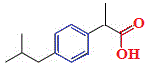
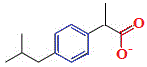


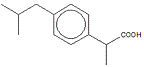
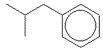 The skeletal formula of 2-methylpropylbenzene is shown on the right.
The skeletal formula of 2-methylpropylbenzene is shown on the right.